Disclosure:
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!
Some of the links on this website are affiliate links. This means that if you click on the link and make a purchase, we may receive a small commission at no extra cost to you. Your support helps us keep the site running.Learn more on my Privacy Policy and Affiliate Disclosure page. Thank you for your support!

Taking charge of your health is a powerful act of self-care, and for women, this means staying informed about crucial screenings and preventive measures. Throughout our lives, our bodies undergo various changes, and understanding these shifts allows us to make proactive choices that promote well-being and longevity. This comprehensive guide will navigate the essential screenings and preventive measures women need at every stage of life.
Health screenings for women are about staying ahead of the curve. Regular check-ups and tests help catch potential health issues before they become big problems. Being informed isn’t just smart; it’s empowering.
Why Preventive Care Matters
Preventive care is the cornerstone of good health. It encompasses a range of actions aimed at preventing disease, detecting health issues early, and promoting overall wellness. For women, this includes regular checkups, screenings, healthy lifestyle choices, and proactive health management.
Screenings are particularly vital. They are tests designed to detect potential health problems before symptoms arise. Early detection often leads to more effective treatment, better outcomes, and even life-saving interventions. By staying informed and taking the necessary steps, women can significantly reduce their risk of developing serious health conditions and improve their quality of life.
For more tips on cultivating a healthy lifestyle, check out our post on 7 Simple Wellness Habits That Will Transform Your Life In 30 Days-Understanding the science of morning routines can really drive this point home.
Screenings and Preventive Measures by Age Group
A. Adolescence and Young Adulthood (13-29 years)
This phase of life marks a period of significant physical and emotional development. Key screenings and preventive measures during this time include:
- HPV Vaccination: The Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a common sexually transmitted infection that can lead to cervical cancer and other cancers. The HPV vaccine is highly effective in preventing these diseases. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends the HPV vaccine for all girls and boys starting at age 11 or 12, although it can be given as early as age 9. ([invalid URL removed])
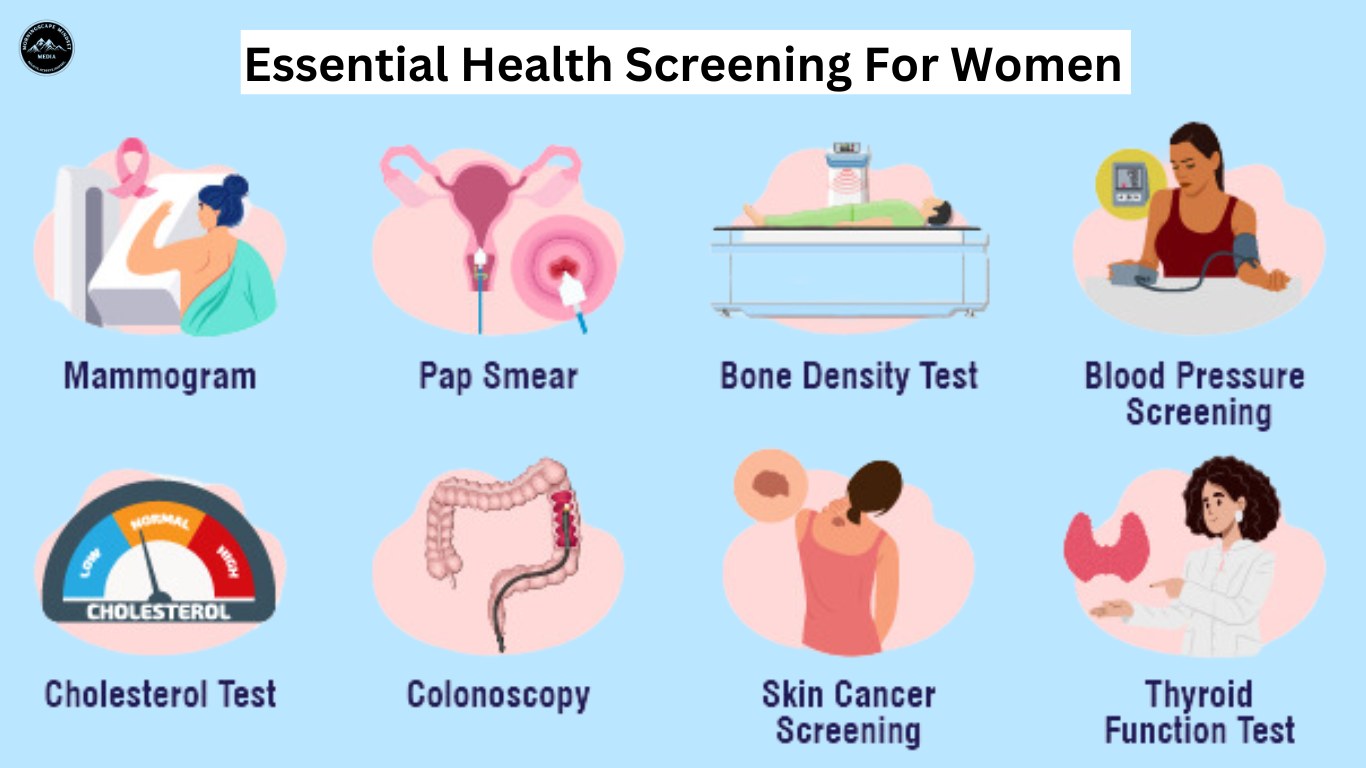
- Pap Smears: This simple test screens for cervical cancer by detecting abnormal cells on the cervix. The recommended starting age for Pap smears is 21, and they should be repeated every three years for women aged 21-29.
- STI Screenings: Sexually active young women should discuss STI screening with their healthcare provider. Regular testing for infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea is crucial for early detection and treatment, preventing potential long-term complications.
- Mental Health Screenings: Mental health is just as important as physical health. Young women should be aware of common mental health conditions like depression and anxiety. Regular checkups with a healthcare provider can help identify potential concerns and provide access to appropriate support and resources.
Read next:
B. Adulthood (30-49 years)
As women enter their 30s and 40s, new health considerations emerge. Key screenings and preventive measures during this period include:
- Mammograms: Breast cancer is a significant concern for women. Mammograms are X-ray images of the breasts that can detect cancer early, even before it can be felt. The recommended frequency of mammograms varies depending on individual risk factors and family history. Generally, women should start getting mammograms every one to two years starting at age 40.
- Cholesterol Checks: High cholesterol can increase the risk of heart disease, a leading cause of death for women. Regular cholesterol checks, typically starting at age 20, can help monitor levels and identify any necessary lifestyle changes or medical interventions.
- Blood Pressure Monitoring: High blood pressure (hypertension) is another major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Regular blood pressure checks are essential for early detection and management.
- Skin Cancer Screenings: Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States. Regular self-exams and skin checks by a dermatologist can help detect suspicious moles or lesions early, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
check out mayo clinic Routine screening tests for women as they enter midlife and beyond– As you near middle age, you may dread that “it’s-time-for-your-first-colonoscopy” talk — and wonder what exactly will happen and why.
C. Midlife and Beyond (50+ years)
Menopause and aging bring new health challenges. Key screenings and preventive measures during this phase include:
- Colonoscopy: Colorectal cancer is a leading cause of cancer death in women. A colonoscopy allows a doctor to examine the colon for polyps or abnormalities. Regular colonoscopies, starting at age 50, can help detect and prevent colorectal cancer.
- Bone Density Scan: Osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones, becomes more prevalent with age, especially after menopause. A bone density scan measures bone mineral density and helps assess the risk of fractures.
- Diabetes Screening: The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age. Regular diabetes screenings, especially for women with risk factors like obesity or family history, can help detect the condition early and manage it effectively.
- Eye Exams: Age-related vision changes and eye diseases like glaucoma and macular degeneration become more common after age 50. Regular eye exams can help detect these conditions early and preserve vision.
Lifestyle Factors and Preventive Measures
While screenings are crucial, healthy lifestyle choices are equally important for preventing disease and promoting well-being throughout life:
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein provides the essential nutrients for optimal health. Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats can reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity offers numerous benefits, including maintaining a healthy weight, reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some cancers, and improving mental health and mood. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.To learn more about the SLU Expert Offers 7 Tips to Maintain a Healthy Gut click the link.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can take a toll on physical and mental health. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature, is essential for overall well-being.
- Sleep Hygiene: Quality sleep is crucial for physical and mental restoration. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night and practice good sleep hygiene habits, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing your sleep environment.
- Substance Use: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use can have serious health consequences. Avoiding or quitting these habits can significantly reduce the risk of various diseases and improve overall health.
Mental Health
Mental health is an integral part of women’s overall well-being. It’s important to prioritize mental health and seek support when needed.
- Mental Health Awareness: Recognize the signs and symptoms of common mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, and postpartum depression. Don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider or mental health professional if you’re struggling.
- Common Mental Health Conditions: Depression, anxiety, and postpartum depression are common among women. These conditions can significantly impact quality of life, but effective treatments are available. Seek professional help if you’re experiencing symptoms.
- Self-Care Strategies: Prioritize self-care to manage stress and promote mental well-being. This might include activities like exercise, meditation, spending time with loved ones, pursuing hobbies, or engaging in relaxing activities.
find out more on University Of California Women’s Preventive Health-Leaders in Women’s Preventive Health Services.
Building a Relationship with Your Healthcare Provider
A strong relationship with your healthcare provider is essential for proactive health management.
- Finding the Right Provider: Choose a healthcare provider you trust and feel comfortable with. Consider factors like their communication style, experience, and approach to patient care.
- Open Communication: Be open and honest with your provider about your health concerns, lifestyle habits, and any symptoms you may be experiencing. Ask questions and actively participate in your healthcare decisions.
- Advocating for Your Health: Be proactive in your healthcare and advocate for your needs. Don’t hesitate to ask for clarification, seek second opinions, or request referrals if necessary.
explore more:
Conclusion
By prioritizing preventive care, women can take control of their health and significantly reduce their risk of developing serious health conditions. Stay informed about the recommended screenings and preventive measures for your age group, and make healthy lifestyle choices a priority. Remember, investing in your health is an investment in your future.
Sometimes, accessing screenings can be tricky due to various barriers. Fortunately, many communities work to lessen these through better awareness and affordable healthcare options. It’s key to seek out available resources to make health screenings a regular part of life.
Recommended Resource
For comprehensive information on women’s health topics, visit the Office on Women’s Health website: https://www.womenshealth.gov/
more about:
health / fitness / wellness / nutrition
SHARE THIS ARTICLE













