Disclosure:
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!
Some of the links on this website are affiliate links. This means that if you click on the link and make a purchase, we may receive a small commission at no extra cost to you. Your support helps us keep the site running.Learn more on my Privacy Policy and Affiliate Disclosure page. Thank you for your support!
Introduction to Gut Health: Why It Matters
Gut health is the foundation of overall wellness, influencing everything from digestion to immunity and even mood regulation. Often called the “second brain,” the gut contains trillions of microorganisms – collectively known as the microbiome – which play a key role in maintaining health. In this guide, we’ll delve into the foods, habits, and tips you need to support a balanced microbiome and promote optimal gut health.
What Is the Microbiome?
The microbiome is a collection of microorganisms living in the intestines, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. While “bacteria” might sound negative, many of these microbes are beneficial and work together to keep the gut functioning properly. A healthy microbiome aids digestion, synthesizes essential nutrients, strengthens the immune system, and even produces neurotransmitters that affect mood.
The Link Between Gut Health and Overall Wellness

The gut’s impact goes far beyond digestion. Research has shown that a balanced microbiome can reduce inflammation, regulate metabolism, and support cognitive function. Conversely, an imbalanced gut microbiome (dysbiosis) can lead to digestive issues, weakened immunity, and increased susceptibility to chronic diseases like diabetes, obesity, and even mental health disorders like anxiety and depression## Best Foods for Gut Health: What to Eat and Why
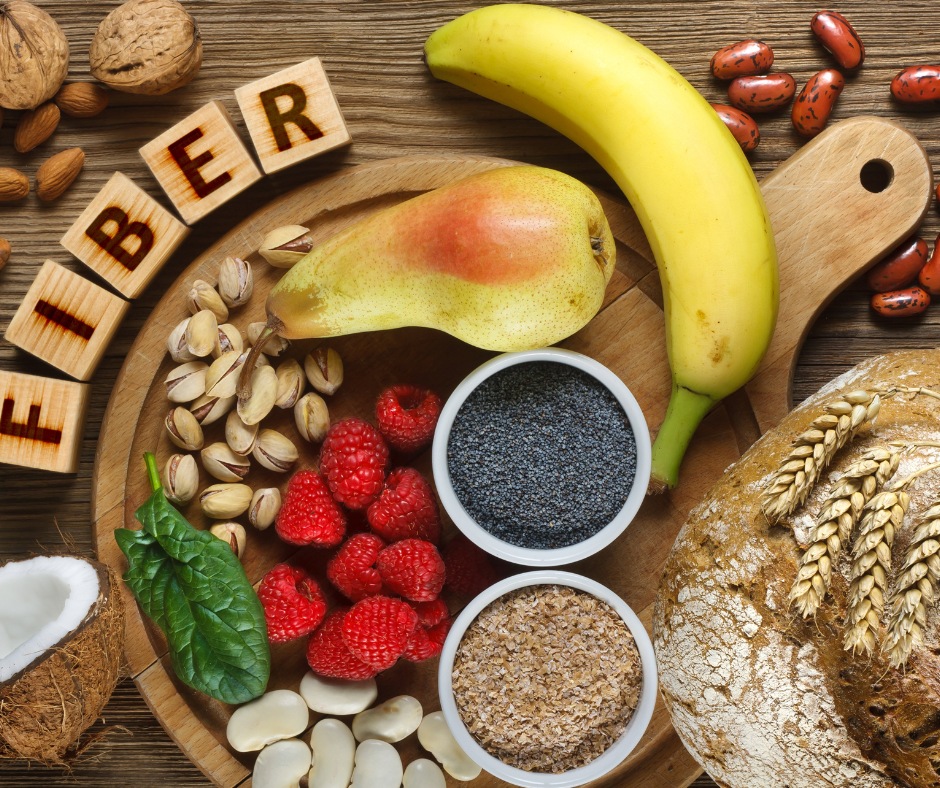
1. Fiber-Rich Vegetables and Fruits
Fiber serves as a prebiotic, providing “food” for beneficial bacteria in the gut. Foods high in fiber, such as leafy greens, apples, carrots, and berries, promote a diverse microbiome, which is essential for gut balance. Notably, fiber also helps move waste through the digestive system efficiently.
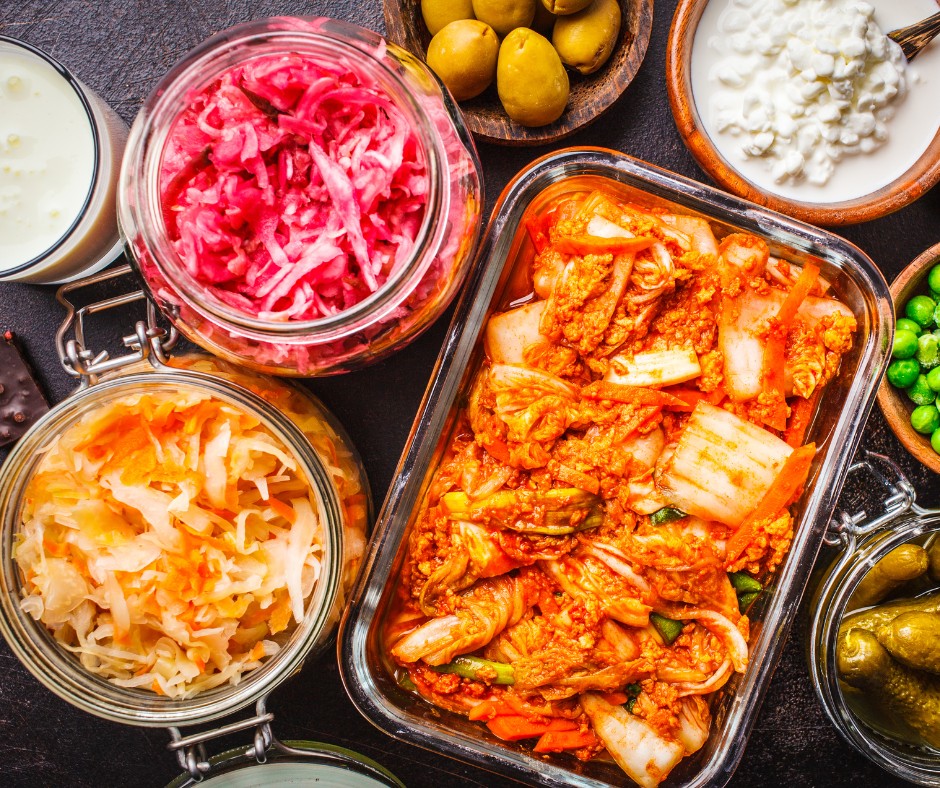
2. Fermented Foods
Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha are excellent sources of probiotics. Probiotics are live bacteria that replenish and diversify the gut microbiome, aiding digestion and enhancing immunity . Try ing a daily serving of one or more fermented foods for lasting gut health benefits.

3. Whole Grains
Whole grains such as oats, barley, and quinoa contain prebiotics and fiber, which nourish beneficial gut bacteria and help maintain steady energy levels. Whole grains can also aid in regularity and improve the overall gut environment.
4. Legumes and Beans
Legumes, including lentils, chickpeas, and black beans, are not only packed with fiber but also rich in resistant starch, which passes undigested into the colon where it ferments, feeding healthy gut bacteria. Studies have shown that legumes contribute to a more diverse and resilient microbiome.
5. Polyphenol-Rich Foods
Foods high in polyphenols, like berries, green tea, and dark chocolate, support beneficial bacteria and reduce inflammation in the gut. Polyphenols have antioxidant properties, which help protect the gut lining and reduce inflammation throughout the digestive system.
Foods to Limit for Optimal Gut Health
While nourishing your gut, it’s also essential to limit foods that disrupt microbiome balance. Processed foods, added sugars, and excessive alcohol can feed harmful bacteria, causing dysbiosis. Artificial sweeteners, often used in diet sodas, have also been linked to negative changes in gut bacteria, so avoiding or limiting these can further support gut health.
Habits for a Healthy Gut Microbiome
1. Prioritize Sleep
Quality sleep is fundamental for gut health. Research shows that sleep deprivation can negatively affect the microbiome, increasing harmful bacteria. Aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep per night to support a balanced microbiome.
2. Manage Stress Levels
Chronic stress can alter the composition of gut bacteria, impacting digestion and immunity. Incorporating stress-management practices such as mindfulness, deep breathing, and regular physical activity can keep stress in check and support gut health. Explore our recent guide on managing stress effectively for more tips morning routine for stress relief.
3. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity not only benefits physical fitness but also promotes gut health by enhancing microbiome diversity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, to support your gut.
4. Hydrate Adequately
Water helps keep everything in the digestive tract moving smoothly, which supports the microbiome and prevents constipation. Aim for 8 glasses of water daily, more if you’re active or in a warm climate.
Tips to Strengthen Gut Health and Improve Digestion
Introduce New Foods Gradually: If you’re adding more fiber or fermented foods to your diet, introduce them slowly to prevent digestive upset.
Eat Smaller, Balanced Meals: Large meals can overwhelm digestion, while smaller, balanced meals can help maintain gut comfort and nutrient absorption.
Listen to Your Gut: Pay attention to foods that may cause discomfort or digestive issues, as individual responses to foods vary.
When to Consider Probiotics and Prebiotics
Sometimes, lifestyle and diet changes may need additional support. Probiotic supplements can be beneficial, especially if you’re taking antibiotics, which can disrupt the microbiome. Look for probiotics with diverse strains for comprehensive support. Prebiotic supplements, typically in fiber form, can also help by feeding beneficial bacteria already present in the gut. Speak with a healthcare provider to determine if these supplements are right for you.
The Connection Between Gut Health and Mental Well-being
Did you know that gut health directly impacts mental well-being? Often referred to as the gut-brain axis, this connection explains how gut bacteria produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, which affect mood and emotional health . A balanced gut o improved mental clarity, reduced stress, and enhanced mood stability.
Key Takeaways and Final Tips for a Healthier Gut
A healthy gut microbiome is within reach through mindful dietary choices, regular exercise, proper hydration, and stress management. By prioritizing these habits, you can create a supportive environment for beneficial bacteria and enjoy long-term health benefits that go beyond the gut.
Start Your Gut Health Journey Today!
Transforming your gut health doesn’t happen overnight, but small, consistent changes make a difference. Start incorporating more fiber, fermented foods, and gut-friendly habits today to experience the benefits of a balanced microbiome. To continue learning about wellness topics, subscribe to our newsletter on holistic health tips and wellness insights.
For further reading, check out our comprehensive guide on sleep and wellness or explore the benefits of exercise for mental health on Harvard Health.
more about:
HEALTH / WELLNESS / FITNESS / NUTRITION
share the article







